How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of drone operation, from understanding FAA regulations and pre-flight checks to mastering flight controls and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover essential safety procedures, troubleshooting common issues, and best practices for post-flight maintenance, ensuring you’re well-equipped to take to the skies responsibly and confidently.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or have some prior experience, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to operate a drone safely and efficiently. We’ll delve into the intricacies of drone flight, covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, all while emphasizing the importance of adhering to regulations and prioritizing safety.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to relevant regulations and safety protocols. Failure to do so can result in fines, legal action, and potentially endanger others. This section covers key aspects of safe and legal drone operation.
FAA Regulations for Drone Operation
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States governs drone operation. Airspace is classified into various classes, each with specific regulations. Understanding these classes is crucial for safe and legal flight. For example, Class G airspace, generally uncontrolled airspace below 1,200 feet, has less stringent requirements than Class B airspace, which surrounds major airports and requires authorization for drone operation.
Specific regulations also exist regarding drone weight, registration, and operational limitations such as distance from airports or populated areas.
Drone Flight Safety Procedures
Safe drone operation involves a comprehensive approach encompassing pre-flight, in-flight, and post-flight procedures. Consistent adherence to these procedures minimizes risks and ensures the safety of the drone, the operator, and the surrounding environment.
- Pre-flight: This includes thorough inspection of the drone’s components, battery checks, GPS calibration, and reviewing weather conditions.
- In-flight: Maintaining visual line of sight with the drone, avoiding obstacles, and being aware of surrounding airspace are essential.
- Post-flight: Safely landing the drone, powering it down, and storing it properly are crucial steps to prevent damage and ensure longevity.
Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
A thorough pre-flight inspection is paramount for safe operation. This checklist helps ensure all critical components are functioning correctly before takeoff.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and a solid understanding of its controls; for a comprehensive guide, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, safe and responsible drone operation is paramount for both personal safety and legal compliance.
- Battery charge level
- Propeller condition and tightness
- Camera functionality
- GPS signal strength
- Controller connection
- Gimbal functionality (if applicable)
Drone Certifications and Requirements
Different levels of drone certifications exist, each with varying requirements and flight restrictions. Understanding these differences is crucial for legal and responsible operation.
| Certification | Requirements | Flight Restrictions | Penalties for Violations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recreational | Registration (in some cases), adherence to basic safety guidelines | Limited to recreational purposes, specific airspace restrictions | Warnings, fines |
| Part 107 (Commercial) | FAA written exam, background check, recurrent training | Depends on specific authorization; may include operating near airports or in restricted airspace | Significant fines, license suspension or revocation |
| Other Specialized Certifications | Varies depending on specific needs (e.g., law enforcement, aerial photography) | Varies depending on the specific certification and its authorization | Varies depending on the severity of the violation |
Pre-Flight Preparations
Proper pre-flight preparation is essential for a safe and successful drone flight. This involves a systematic approach to ensure the drone is ready for operation and the pilot is prepared for flight.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of the fundamentals, and a great resource to help you learn is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to safely and effectively control your drone, ensuring a positive flying experience.
Step-by-Step Drone Flight Preparation
- Charge the drone’s battery to the recommended level.
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage.
- Power on the drone and controller, ensuring a proper connection.
- Calibrate the compass and GPS.
- Check the drone’s propellers for damage or looseness.
- Verify the camera is functioning correctly.
- Review the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Plan the flight path and identify potential hazards.
Compass and GPS Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s compass and GPS is crucial for accurate flight and stability. Inaccurate calibration can lead to erratic flight behavior or loss of control. The specific calibration procedure varies by drone model but typically involves rotating the drone slowly in a figure-eight pattern.
Pre-Flight Component Checklist
This checklist ensures all essential drone components are in good working order before flight.
- Propellers
- Camera
- Gimbal (if applicable)
- Battery
- Antenna
- Remote controller
Essential Drone Tools and Accessories
Having the right tools and accessories enhances the drone operation experience and enables effective maintenance.
- Spare batteries
- Propeller removal tool
- Screwdrivers
- Carrying case
- Cleaning cloth
- Calibration tools (if needed)
Taking Off and Landing
Safe and controlled takeoff and landing procedures are crucial for preventing accidents and damage. This section details proper techniques for various situations.
Takeoff Procedure, How to operate a drone
A smooth and controlled takeoff involves several steps. First, ensure the drone is in a clear, open area, away from obstacles and people. Then, carefully lift the drone using the throttle, maintaining stability. Monitor the drone’s altitude and orientation, making any necessary adjustments. Avoid sudden movements.
Landing Techniques
Landing techniques vary depending on the terrain and wind conditions. In calm conditions, a slow, controlled descent is ideal. In windy conditions, adjusting the throttle and using the directional controls to maintain stability is essential. Always ensure a clear and safe landing area.
Takeoff and Landing Methods Comparison
Different drone models may have slightly different takeoff and landing procedures. Some drones offer automated takeoff and landing features, while others require more manual control. Understanding your specific drone’s capabilities is crucial.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Zones
Imagine a circle, approximately 10-15 feet in diameter, marked on a flat, level surface, free from obstacles like tall grass, rocks, or wires. The circle represents the ideal landing zone. The area surrounding the circle, extending another 10-15 feet in all directions, should also be clear of obstacles to provide ample space for takeoff and landing maneuvers. The surface should be firm enough to support the drone’s weight without sinking or causing instability.
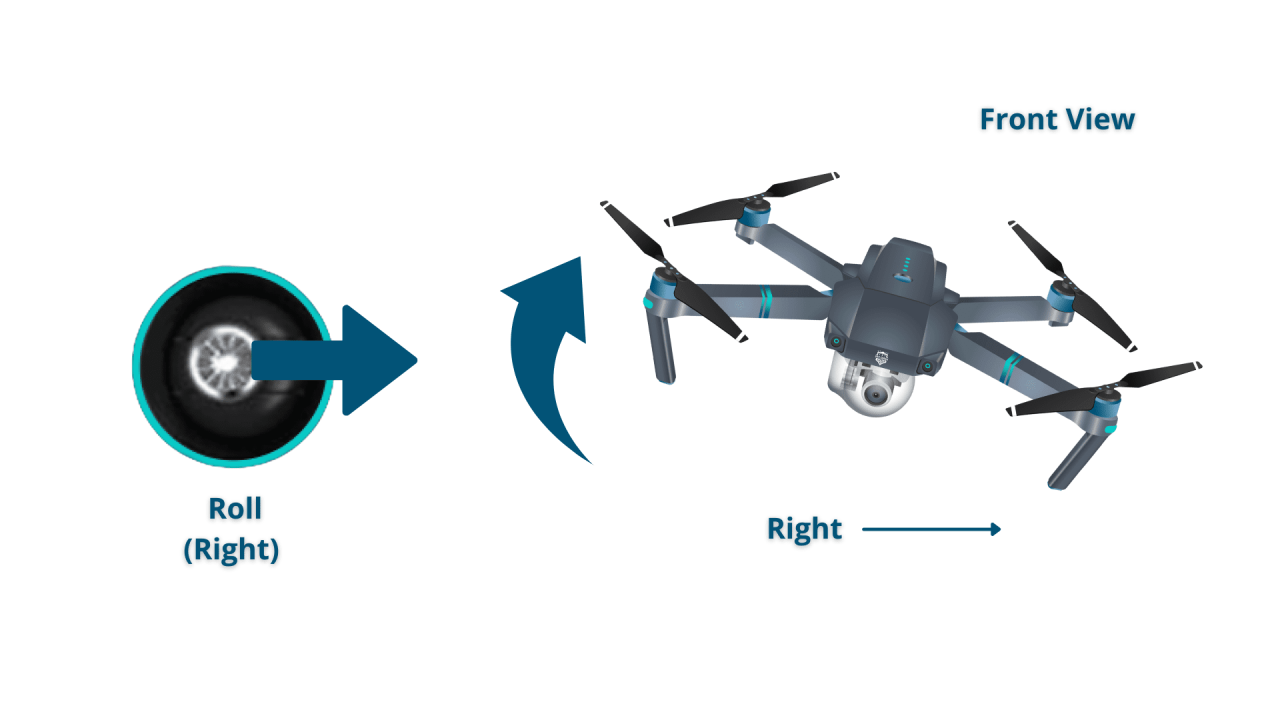
Drone Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding drone flight controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section explains basic and advanced maneuvers.
Drone Remote Control Functions
Most drone remotes have two control sticks: one for controlling the drone’s altitude and direction, and the other for controlling its lateral movement. Buttons on the remote usually control functions like camera operation, return-to-home, and emergency stops. The specific functions and layout vary by drone model, so consulting your drone’s manual is crucial.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Basic maneuvers include hovering, ascending, descending, and turning. Mastering these is essential before attempting more advanced maneuvers. Practice in a safe, open area to develop smooth and controlled movements.
Common Mistakes of Novice Drone Pilots
Common mistakes include losing visual line of sight, flying too close to obstacles, neglecting battery life, and failing to check weather conditions. These mistakes can lead to accidents and damage.
Advanced Maneuvers

Advanced maneuvers, such as precise hovering and smooth camera movements, require practice and skill. These maneuvers are essential for professional-quality aerial photography and videography. They often involve fine adjustments of the control sticks and careful coordination with the camera controls.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography
Capturing high-quality aerial footage requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. This section provides guidance on optimizing image quality.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture significantly impact image quality. Understanding how these settings interact and affect exposure, depth of field, and motion blur is key to capturing sharp, well-exposed images and videos.
Camera Modes and Applications
Different camera modes, such as photo, video, and timelapse, offer diverse creative possibilities. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each mode allows for informed choices depending on the desired outcome.
Tips for High-Quality Aerial Photography and Videography
Tips for high-quality results include maintaining stable flight, using appropriate lighting, and planning shots carefully. Experimentation and practice are crucial to develop a keen eye for composition and capturing stunning aerial footage.
Examples of Drone Shot Compositions
- High-angle shot: Shows a wide view of the subject from above.
- Low-angle shot: Creates a dramatic perspective by shooting from below.
- Tracking shot: Follows a moving subject, creating a dynamic visual.
- Aerial panorama: Stitches multiple photos together to create a wide, panoramic view.
- Dutch angle: Tilts the camera to create a sense of unease or disorientation.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Understanding common drone malfunctions and troubleshooting techniques is essential for maintaining operational readiness. This section provides guidance on resolving common problems.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common issues include low battery, GPS signal loss, motor failure, and communication problems. Understanding the potential causes of these problems is the first step towards effective troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting Steps for Common Problems
Troubleshooting steps often involve checking connections, restarting the drone and controller, and verifying battery levels. More complex issues may require more advanced diagnostics or professional assistance.
Common Error Messages and Solutions
| Error Message | Possible Cause | Troubleshooting Steps | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Insufficient battery charge | Check battery level, charge battery | Replace with a fully charged battery |
| GPS Signal Lost | Obstructed GPS signal, interference | Move to an open area with clear sky view | Relocate to a suitable location |
| Motor Failure | Motor malfunction, damaged propellers | Inspect motors and propellers | Replace faulty motors or propellers |
| Communication Error | Weak signal, interference | Check distance between drone and controller, reduce interference | Move closer to the drone or reduce interference sources |
Importance of Regular Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance, including cleaning, inspection, and component replacement, extends the drone’s lifespan and minimizes the risk of malfunctions.
Post-Flight Procedures

Proper post-flight procedures are crucial for the safety and longevity of the drone. This section Artikels best practices for safe storage and maintenance.
Safe Landing and Power Down
A safe landing involves a controlled descent to a designated area, followed by powering down the drone and controller in the correct sequence to prevent damage or unexpected behavior.
Drone and Accessory Storage
Proper storage protects the drone from damage and extends its lifespan. This includes storing it in a dry, clean environment, away from extreme temperatures and direct sunlight. Batteries should be stored separately and charged appropriately.
Reviewing Flight Logs
Reviewing flight logs helps identify areas for improvement in piloting skills and flight planning. This contributes to safer and more efficient flights in the future.
Post-Flight Checklist
This checklist ensures all necessary post-flight steps are completed to maintain the drone’s safety and longevity.
- Safely land the drone.
- Power down the drone and controller.
- Inspect the drone for any damage.
- Clean the drone and its components.
- Store the drone and its accessories properly.
- Review flight logs and identify areas for improvement.
- Charge batteries appropriately.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. By diligently following safety protocols, understanding flight mechanics, and consistently practicing, you can unlock the full potential of your drone. Remember, responsible drone piloting not only ensures your safety and the safety of others but also helps maintain a positive image for the entire drone community.
So, get ready to take flight, and remember to always fly safely and responsibly!
Frequently Asked Questions: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and autonomous features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good flight time and ease of control.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’re flying in areas with strong magnetic interference.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal during flight?
Immediately switch to manual control and attempt to bring the drone back to the takeoff point. If unable, land it safely in a clear area.
How do I register my drone with the FAA?
Visit the FAA’s website (faa.gov) for registration requirements and procedures. Registration is typically required for drones weighing over 0.55 pounds.
